Table of Contents
One of the most talked-about concepts of the 21st century is cryptocurrency and the ever-expanding crypto market. However, the idea remains intimidating and incomprehensible for many. This blog is an easy-to-follow tutorial for learners that aims to clarify what cryptocurrency is, how it operates within the crypto industry, and why it’s changing financial services..
Cryptocurrency is an instrument of virtual or digital money that is encrypted by secure communication. Cryptocurrencies depend on decentralised networks based on blockchain technology, in contrast to fiat currencies, which is conventional money issued by governments. It also suggests that it is not governed by a single entity, such as a government or bank.
Understanding the Digital Revolution
- Decentralization: Managed by peer-to-peer networks instead of a single authority.
- Security: Transactions are secured using complex cryptographic algorithms.
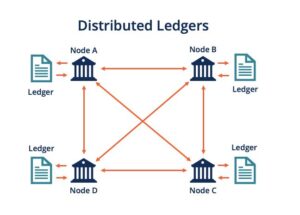
- Transparency: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger known as the blockchain.
Limited Supply: Most cryptocurrencies have a fixed supply, which can make them resistant to inflation.
Popular Cryptocurrencies:
- Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most well-known cryptocurrency.
- Ethereum (ETH): Known for its smart contract functionality.
- Binance Coin (BNB), Cardano (ADA), and Solana (SOL): Other prominent cryptocurrencies with unique features.
What is the Method of Cryptocurrency:
Blockchain technology enables cryptocurrency. A distributed ledger that records the track of every transaction made via a network of computers is called a blockchain. When a transaction made with bitcoin is sent, it is stored on the blockchain, confirmed by network users (also referred to as miners or validators), and cannot be changed subsequently. This transparent and tamper-proof system is one of the key reasons why investment in cryptocurrency has gained global attention.
How to Get Started:
- Choose a Cryptocurrency Exchange:
Platforms like Coinbase, Binance, or Kraken allow you to buy, sell, and trade crypto.
2. Create and Secure Your Wallet:
A crypto wallet stores your digital assets. It can be a software wallet (online or mobile) or a hardware wallet (offline).
3. Buy Your First Cryptocurrency:
Start small and diversify your investments.
4. Stay Informed:
Follow reputable news sources and community discussions to keep up with market trends and security tips.
Risks and Considerations:
- Volatility:
Cryptocurrency prices can be highly volatile.
- Security Risks:
Hacking and scams are prevalent.
- Regulatory Uncertainty:
Laws and regulations around crypto vary by country and are still evolving.

Market Capitalization:
Market Cap is a simple but powerful formula in cryptocurrency (and traditional stocks too).
It helps you quickly estimate how much a coin or project is worth in total.
Here’s the basic formula:
Market Cap=Current Price×Circulating Supply\text{Market Cap} = \text{Current Price} \times \text{Circulating Supply}Market Cap=Current Price×Circulating Supply
Where:
- Current Price = the price of one unit of the coin/token.
- Circulating Supply = the number of coins/tokens that are publicly available and circulating in the market (NOT the maximum supply).
Example:
Suppose:
- The current price of a coin = $2
- The circulating supply = 10 million coins
Then:
Market Cap=2×10,000,000=20,000,000 USD\text{Market Cap} = 2 \times 10,000,000 = 20,000,000 \, \text{USD}Market Cap=2×10,000,000=20,000,000 USD
How to Analyze Using Market Capitalization Formula:
Compare Projects:
A high market cap usually means a project is more “established” or “widely trusted.”
A lower market cap might indicate “higher risk, higher reward” potential, but also more volatility.
Identify Growth Potential:
If a project has a low market cap and strong fundamentals (good tech, strong team, real utility), it might have more room to grow compared to a “blue-chip” crypto like Bitcoin.
Understand Dilution Risk:
Some projects have a small circulating supply but a huge total supply. Future unlocking of coins can dilute value — meaning the price might drop as more coins come into circulation.
Valuation Reality Check:
Just because a coin is “cheap” (like $0.01) doesn’t mean it’s a good deal. You must check Market Cap — a coin can be cheap per unit but still have a multi-billion-dollar valuation!
In CoinMarketCap (or similar sites):
You’ll often see:
- Market Cap (already calculated)
- Price
- Circulating Supply
You can manually cross-check:
IsPrice×Circulating Supply= Market Cap shown?\text{Is} \quad \text{Price} \times \text{Circulating Supply} \quad \text{= Market Cap shown?}Is Price×Circulating Supply= Market Cap shown?
If not, sometimes self-reported supplies or different sources can slightly vary.
Quick Tip:
You can even rearrange the formula:
Price=Market Cap Circulating Supply\text {Price} = \frac{\text{Market Cap}}{\text{Circulating Supply}}Price=Circulating Supply Market Cap
If you know the future circulating supply target, you can predict future price ranges!
If you know the future circulating supply target, you can predict future price ranges,
I mean you can estimate what the price of a coin could be in the future if you know:
- Future Circulating Supply (when more coins get unlocked, staked rewards, vesting periods end, etc.)
- Market Cap target (for example: “What if this coin grows to a $1 billion market cap?”)
Here’s the Logic:
You already know:
- Price=Market Cap Circulating Supply\text{Price} = \frac{\text{Market Cap}}{\text{Circulating Supply}}Price=Circulating SupplyMarket Cap
- So if the circulating supply increases, the price must adjust if the market cap stays the same.
- If supply increases and market cap stays constant, price decreases.
- If supply increases but market cap grows faster, price can still increase.
Example 1: Supply Increase, Market Cap Constant
- Let’s say:
- Current Circulating Supply = 100 million coins
- Current Market Cap = $1 billion
- So Current Price =
- 1,000,000,000100,000,000=10 USD per coin\frac{1,000,000,000}{100,000,000} = 10 \, \text{USD per coin}100,000,0001,000,000,000=10 USD per coin
- Now, imagine in one year, circulating supply will become 200 million coins (due to unlocking).
- If the Market Cap stays the same ($1 billion), then:
- New Price=1,000,000,000200,000,000=5 USD per coin\text{New Price} = \frac{1,000,000,000}{200,000,000} = 5 \, \text{USD per coin}New Price=200,000,0001,000,000,000=5 USD per coin
Price dropped by half because supply doubled, but market value stayed constant.
Example 2: Supply Increase, Market Cap Grows
- Same situation:
- Future Circulating Supply = 200 million
- But suppose Market Cap grows to $2 billion (because the project succeeded)
- Then:
- New Price=2,000,000,000200,000,000=10 USD per coin\text{New Price} = \frac{2,000,000,000}{200,000,000} = 10 \, \text{USD per coin}New Price=200,000,0002,000,000,000=10 USD per coin
Price stays the same ($10) even though supply doubled, because market cap also doubled.
Why This Matters:
- Future Supply Growth (like token unlock schedules) can put selling pressure on price.
- Good projects might grow their Market Cap enough to offset supply increases.
- Smart investors analyze tokenomics (future supply schedules) before buying!
Real Life: How to Use It
When you research a coin:
- Check Circulating Supply NOW vs. Total Max Supply.
- Find the token unlock schedule (found in whitepapers or sites like Token Unlocks).
- Ask yourself:
“Will there be a lot of new supply hitting the market soon?”
“Can the project grow fast enough to keep the price up?”

What Are Crypto Tax Regulations?
Governments view cryptocurrency in one of three ways depending on the country:
- As property (like real estate or stocks)
- As assets (like commodities)
- Sometimes, even as currency (rare)
Because of that, they tax crypto activities — just like they tax investments.
Earning passive income with cryptocurrency in 2025 offers various opportunities, each with its own risk
1. Staking
involves locking up your crypto assets to support blockchain network operations, earning rewards in return. It is increasingly viewed as a passive income strategy within the broader landscape of investment in cryptocurrency Platforms like Coinbase, Kraken, and Binance offer staking services for various cryptocurrencies.
2. Crypto Lending
By lending your crypto to borrowers through platforms like Nexo or decentralized protocols, you can earn interest. This method allows you to generate income without selling your assets.
3. Yield Farming & Liquidity Mining
Providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap or PancakeSwap can earn you a share of transaction fees and additional token rewards. This strategy often involves higher risk due to market volatility.
4. Dividend-Earning Tokens
Certain cryptocurrencies, such as KuCoin Shares (KCS) and NEO, distribute a portion of their profits to token holders. Holding these tokens can provide regular dividend payouts.
5. Play-to-Earn (P2E) Games
Engaging in blockchain-based games like Axie Infinity allows you to earn crypto rewards through gameplay. While entertaining, this method requires time investment and understanding of the game’s mechanics.
6. Affiliate Programs
Many crypto platforms offer affiliate programs where you earn commissions by referring new users. This strategy is effective if you have a strong online presence or audience, especially when promoting trusted crypto projects through your content.

Important Considerations
- Research Thoroughly: Always conduct due diligence before investing in any platform or strategy.
- Understand Risks: Be aware of market volatility, platform security, and regulatory implications.
- Diversify: Don’t put all your assets into one method; diversify to mitigate risks.
1. Institutional Adoption and Financial Integration
Blockchain is increasingly becoming foundational in traditional financial services. Notably, the adoption of Bitcoin ETFs and the integration of stablecoins into financial systems are reshaping investment and payment landscapes.
2. Tokenization of Real-World Assets (RWA)
The tokenization of physical assets like real estate and precious metals is gaining traction, offering fractional ownership and increased liquidity.
3. Enhanced Interoperability
Efforts are underway to improve interoperability between different blockchain platforms, facilitating seamless asset transfers and data exchange across networks.
4. Evolution of Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi is expanding beyond lending and borrowing to include complex financial instruments like derivatives and insurance, aiming for greater financial inclusion and efficiency.
5. Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) Models
Major tech companies are offering BaaS solutions, enabling businesses to deploy blockchain applications without building infrastructure from scratch, thus accelerating adoption.
6. Green Blockchain Initiatives
With growing environmental concerns, there’s a shift towards energy-efficient consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake, aiming to reduce blockchain’s carbon footprint.
7. Privacy Enhancements
Innovations such as zero-knowledge proofs are being implemented to enhance user privacy and data confidentiality on blockchain networks.
8. Integration with AI and Web 3
The convergence of blockchain with AI and Web 3 technologies is creating decentralized applications that offer users greater control over their data and digital identities.
- Inter-Exchange Arbitrage: Buying a cryptocurrency on one exchange and selling it on another where the price is higher.
- Intra-Exchange (Triangular) Arbitrage: Exploiting price differences between three trading pairs within the same exchange. For example, trading BTC to ETH, ETH to, and USDT back to BTC.
- Spatial Arbitrage: Taking advantage of price discrepancies between exchanges in different geographical locations, considering factors like regional demand and currency exchange rates.
Statistical Arbitrage: mathematical models and algorithms to identify and exploit price inefficiencies across markets.

Tools and Automation
Given the rapid nature of arbitrage opportunities, many traders employ automated trading bots to execute trades swiftly. These bots can monitor multiple exchanges simultaneously and execute trades based on predefined criteria.
Risks and Considerations
- Transaction Fees: Fees for trading and transferring cryptocurrencies can erode profits.
- Transfer Times: Delays in transferring assets between exchanges can result in missed opportunities.
- Market Volatility: Rapid price changes can negate potential profits.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different jurisdictions have varying regulations, which can impact arbitrage strategies.
Key Trends in Blockchain Technology for 2025
1. Institutional Adoption and Financial Integration
Blockchain is increasingly becoming foundational in traditional financial services. Notably, the adoption of Bitcoin ETFs and the integration of stablecoins into financial systems are reshaping investment and payment landscapes.
2. Tokenization of Real-World Assets (RWA)
The tokenization of physical assets like real estate and precious metals is gaining traction, offering fractional ownership and increased liquidity.
3. Enhanced Interoperability
Efforts are underway to improve interoperability between different blockchain platforms, facilitating seamless asset transfers and data exchange across networks.
4. Evolution of Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi is expanding beyond lending and borrowing to include complex financial instruments like derivatives and insurance, aiming for greater financial inclusion and efficiency.
5. Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) Models
Major tech companies are offering BaaS solutions, enabling businesses to deploy blockchain applications without building infrastructure from scratch, thus accelerating adoption.
6. Green Blockchain Initiatives
With growing environmental concerns, there’s a shift towards energy-efficient consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake, aiming to reduce blockchain’s carbon footprint.
7. Privacy Enhancements
Innovations such as zero-knowledge proofs are being implemented to enhance user privacy and data confidentiality on blockchain networks.
8. Integration with AI and Web 3
The convergence of blockchain with AI and Web 3 technologies is creating decentralized applications that offer users greater control over their data and digital identities.
Summary of Key Influencers:
- Vitalik Buterin – Co‑founder of Ethereum, thought leader on protocol design and scaling solutions.
- Michael Saylor – Executive Chairman of Micro Strategy; major institutional Bitcoin advocate.
- Balaji Srinivasan – Former CTO of Coinbase, prolific writer on crypto‑economics and Web 3.
- Camila Russo – Founder of The Defiant, premier DeFi news outlet and author of The Infinite Machine.
- Anthony “Pomp” Pompliano – Investor and host of the Pomp Podcast, focuses on Bitcoin’s macro case.
- Erik Voorhees – CEO of Shape Shift, early Bitcoin entrepreneur and libertarian voice.
- Chris Dixon – General Partner at Crypto, invests in Web 3 startups and shares deep analyses.
- Roger Ver – “Bitcoin Jesus,” early Bitcoin adopter and Bitcoin Cash proponent.
- Andreas M. Antonopoulos – Educator and author of Mastering Bitcoin, expert on security and decentralization.
- Lark Davis – You Tuber and market analyst, known for clear technical breakdowns and altcoin coverage.

Where Crypto Stands Today and Tomorrow
Cryptocurrency has evolved from an experimental digital currency into a recognized asset class that increasingly coexists with traditional finance. Over the past decade, Bitcoin alone has appreciated some 700×, drawing institutional investors via vehicle‑like ETFs and prompting major banks to integrate crypto services into their offerings Axios. While “digital gold” narratives hold for Bitcoin, other sectors—DeFi, NFTs, play‑to‑earn gaming—are still searching for a sustainable product‑market fit.
Regulatory frameworks are tightening globally: the UK’s FCA is set to ban crypto purchases on borrowed funds to protect retail investors The Guardian, and U.S. legislators are debating comprehensive rules on stablecoins, custodial requirements, and consumer safeguards World Economic Forum. At the same time, tokenization of real‑world assets (from real estate to art) promises to democratize ownership and liquidity, supported by emerging Blockchain‑as‑a‑Service (BaaS) offerings from major cloud providers Corporate Finance Institute.
Energy‑efficient consensus mechanisms (Proof‑of‑Stake, zero‑knowledge proofs) are reducing crypto’s environmental footprint and enhancing privacy, paving the way for broader enterprise adoption Corporate Finance Institute. Interoperability protocols are also maturing, enabling assets and data to flow seamlessly across blockchain networks, which will underpin next‑generation Web 3 applications.
Bottom line:
Crypto is unlikely to supplant fiat currency wholesale, but it is carving out permanent roles—as a store of value, programmable finance layer, and digital‑asset platform. Its future rests on balanced regulation, technical scalability, and real‑world utility.Cryptocurrency is transforming how we think about money, investing, and even the internet itself. With proper education and awareness, beginners can safely explore this revolutionary space.

